The project
Started in 2024, the research project on Kiwi die-off continues the crop analysis and monitoring activities Actinidia in Lazio and Calabria.
Funded by Elle Esse AOP within the Operational Programme of the CMO of Emilia-Romagna and implemented by TETHYS in collaboration with theUniversity of Calabria, University of Naples and some agricultural companies of the Pontine territory, the project aims to identify the environmental and agronomic factors that contribute to the onset of the phenomenon.
The goal is to define a continuous and objective monitoring system of vegetative state and soil moisture, to support producers in the prevention of water and root stress that they can promote the onset of kiwifruit decline.
The previous stages
The project was launched in 2024 and presented in the opening article The CMO kiwifruit decline project: a step forward in innovation, who illustrated it goals And working methodology, based on module integration Watch And Aqua for the satellite monitoring and the water balance.
In the following months, thewinter update he described the first soil moisture elaborations, with theidentification of areas subject to water stagnation, while thesummer update documented thevegetative evolution of crops And the differences between covered and uncovered plots, with a First assessment of the impact of hail protection on plant water requirements.
Activities in 2025
During an update meeting between the project partners, TETHYS presented the results of activities carried out in the first ten months of 2025.
The work focused on three lines of analysis: the vegetative state of crops, the seasonal water balance, and winter monitoring of soil moisture.
Vegetative state monitoring
Through the form Watch, they were constantly monitored the vegetative vigor indices (NDVI) of the six plots under study.
The anomalie identified during the season have been verified in two phases: first for exclude any atmospheric effects not detected by the system (haze or cloud cover), then with a visual inspection in the field by the producers.
To date, no significant critical issues have been found and the indices show a trend consistent with the physiology of the plants.
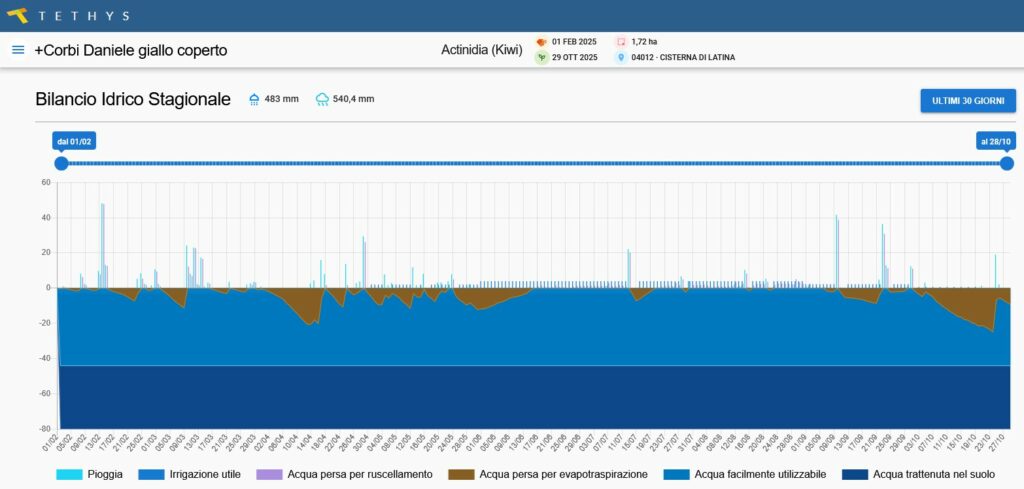
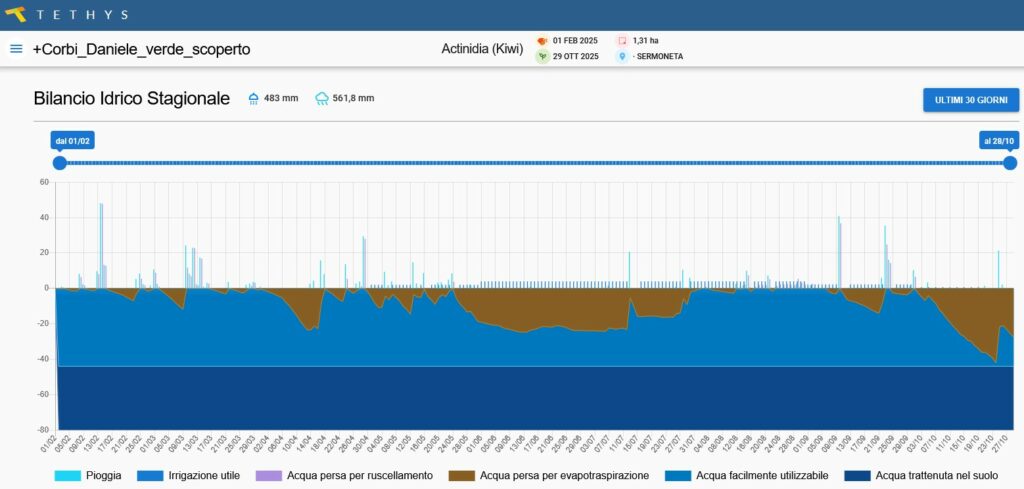
Water balance analysis
The processing of the form Aqua have affected two plots of land to dateDaniele Corbi farm in Sermoneta (LT), specialized in production of green and yellow kiwifruit.
The comparison between actual irrigation volumes and the needs estimated by Aqua highlighted a slight overwatering in the'uncovered plot and a more marked excess in the one covered by anti-hail net, where evapotranspiration is naturally lower.
In both cases, however, no symptoms of die-off or root stress were observed, a sign that the excess water did not produce agronomically significant effects.
Winter soil moisture monitoring
During the period between January and March 2025, with Aqua it was analyzedreal evapotranspiration cumulative of a plot of approximately six hectares of theMauro Guzzo company in Borgo Montello (LT), cultivated with Hayward kiwi And without hail cover.
The processing has highlighted three areas with anomalous evapotranspiration values, potentially attributable to water stagnation phenomena.
The identified areas will be subject to field verification, with the aim of validate satellite analyses And improve the calibration of the hydrological model.
Perspectives
Activities will continue in 2026 with the'extension of monitoring to a greater number of companies and the correlation of water and vegetative data with productivity and mortality indicators.
The ultimate goal is to develop predictive tools for irrigation management and the prevention of kiwi decline, to support more sustainable and resilient fruit growing.










Add comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.